Minilab
During the first semester of my master’s degree at Politecnico di Milano, I attended a course called ACTAM. The goal was to literally build anything you wanted, but using the web programming foundations learned in the course.
I had recently left Sanremo (read here) to move to Milan. I still had in mind the setup I used to play with the Spettri, so I decided to build a single configurable module that would condense the various third-party modules I used during concerts.
In the rest of the text I will explain everything step by step, but if you want you can try (from a PC) the module at this link or watch the demo video below.
Hardware configuration
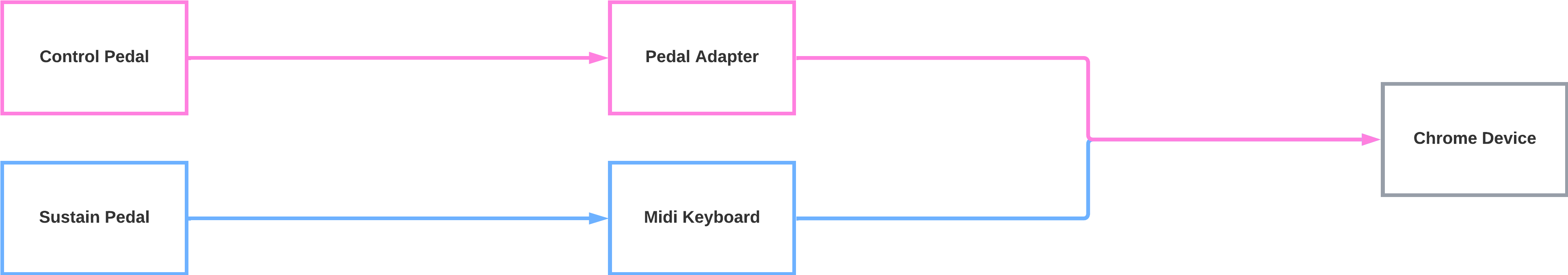
To use all the project features, the following hardware configuration is required:
- Arturia MiniLab MKII –> a small MIDI controller with no internal functions, but equipped with many mappable parameters, ideal for experimentation. You can load the dedicated preset through the Arturia MIDI Control Center app, available here.
- Sustain pedal –> any standard sustain pedal.
- Control pedal adapter –> converts the analog signal to MIDI (for example, this model).
- Control / volume pedal –> any compatible model.
Features
The code implements a software synthesizer that allows combining instruments and effects in real time. The interface lets you select and configure the various instruments, manage the keyboard split, control audio parameters through the knobs, and save your presets on Firebase.
Below you will find a legend of the system interface, followed by the description of the various items.
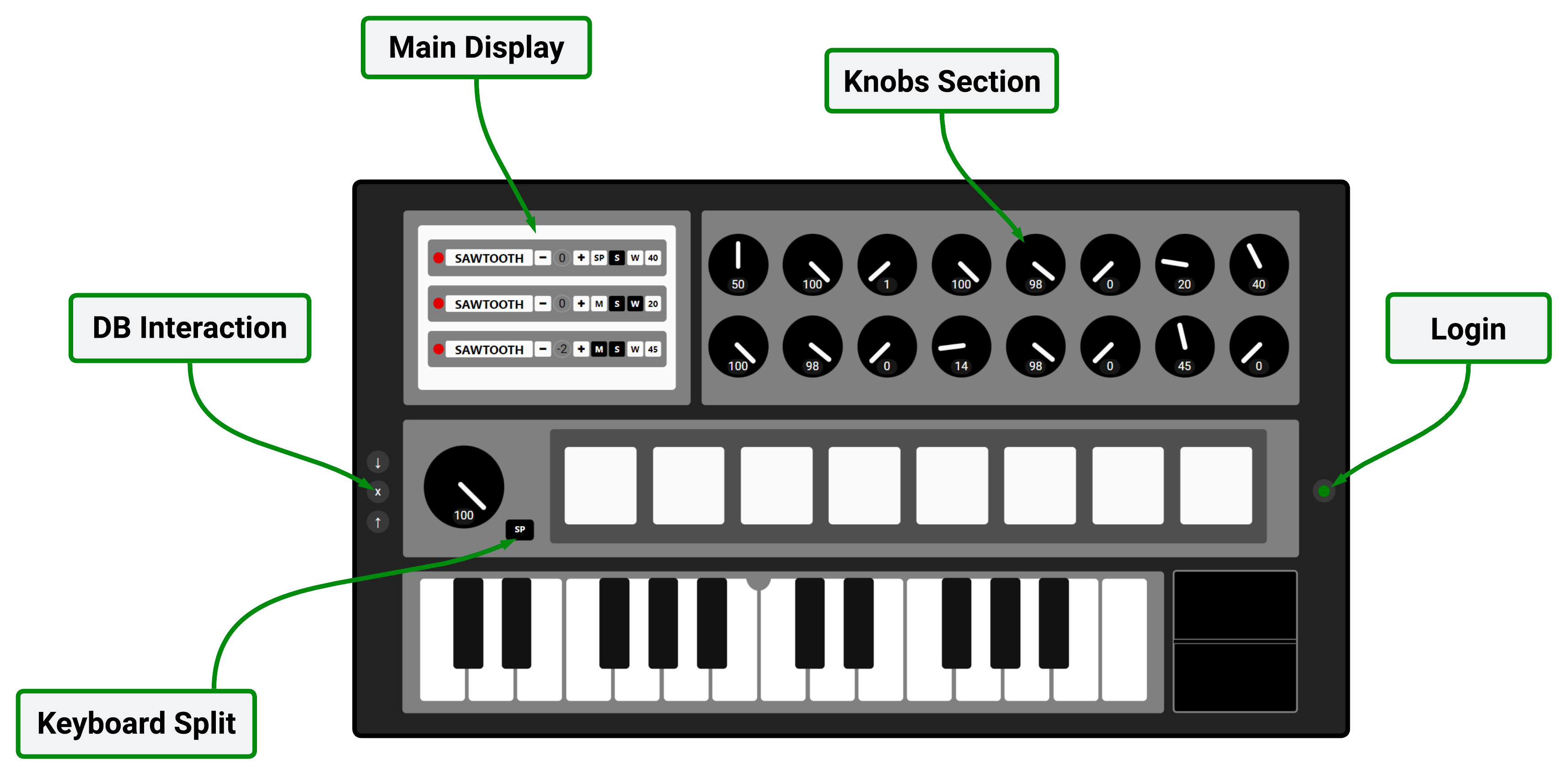
Main Display
From here you select the active instruments: Arpeggiator, Synth1 and Synth2 (respectively for the left and right side of the keyboard, if split). For each one you can change oscillator, mono or polyphonic mode, active MIDI commands, and octave. It is also possible to assign the first two knobs to custom presets, so you can switch configuration quickly during performance.
Keyboard Split
Allows splitting the keyboard into two independent sections, assigning different instruments to the left and right. The arpeggiator can be included in or excluded from the split.
Knobs Section
The knobs allow you to modify sound parameters in real time: overall gains, separate volumes for instruments and drums, LPF and HPF filter cutoff, delay time and volume, and arpeggiator parameters. Each knob can be mapped to the control pedal, with direct, inverted, or disabled mode, for dynamic performance control.
Login
From the Login section you can authenticate via email or anonymously. The DB interaction area allows you to save, load, or delete your presets directly from the cloud.
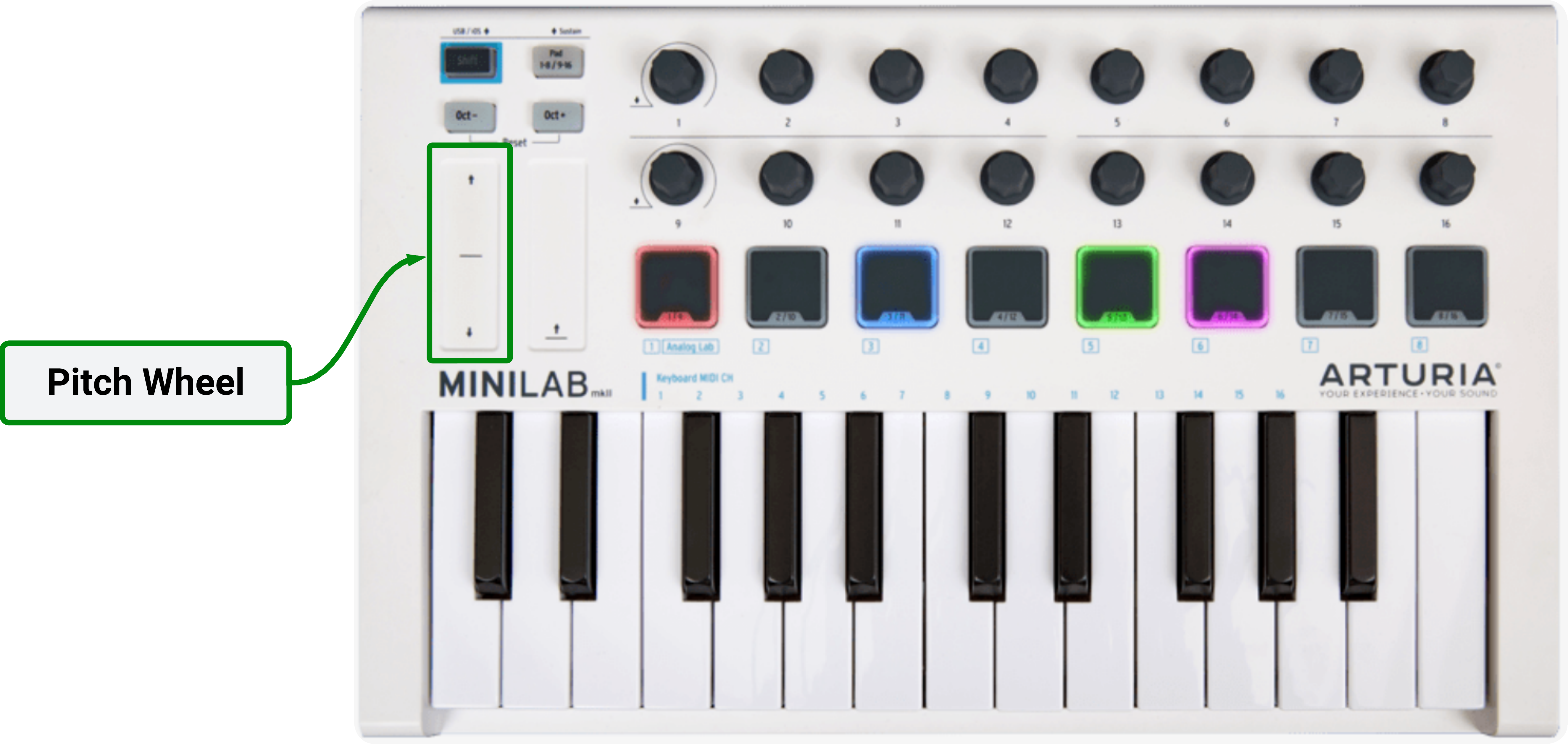
Pitch Wheel
Even though there is no visual indicator, the pitch wheel allows you to change oscillator frequency during performance, achieving very expressive effects when combined with filters and delay.

Code structure
The project is written entirely in JavaScript and uses only the Firebase library for database management. The audio part is entirely based on the Web Audio API, which allows generating, filtering, and visualizing sound in real time.
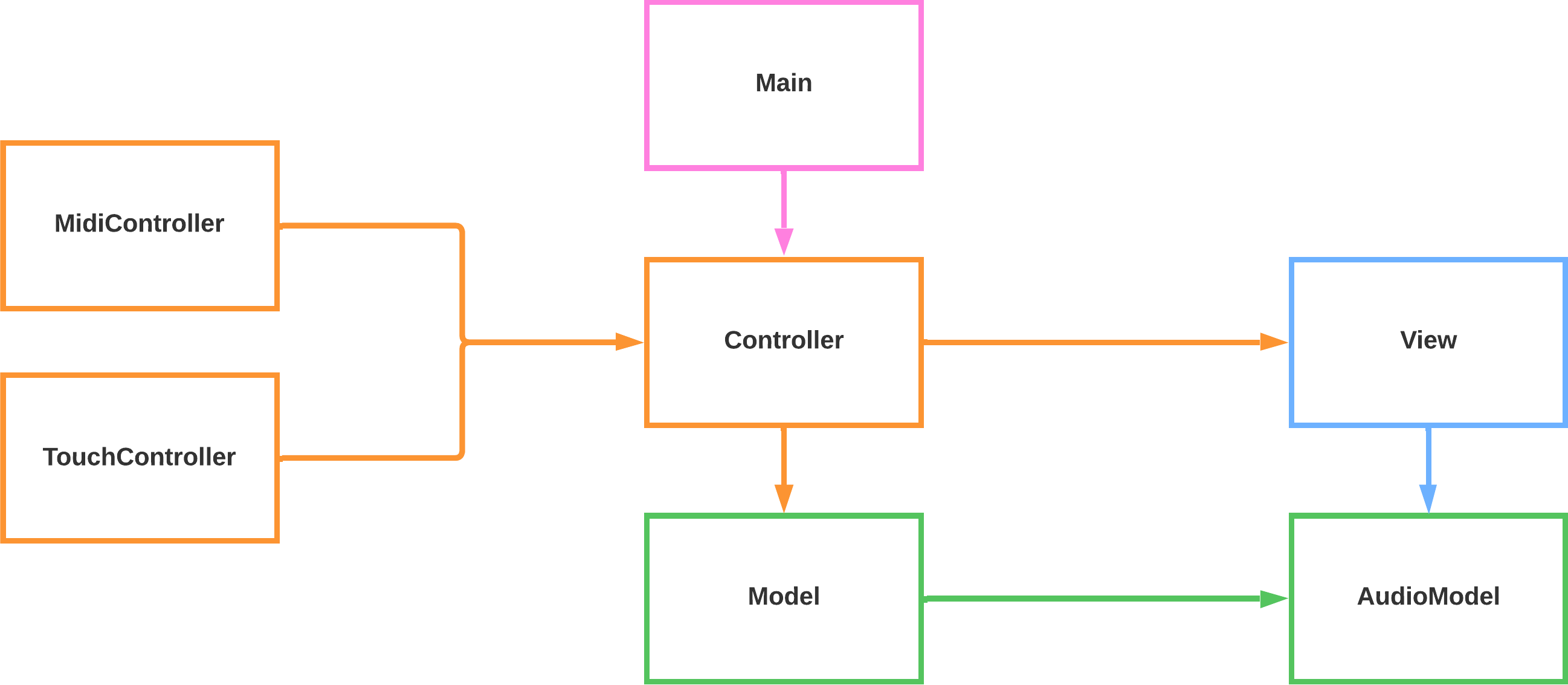
Below I write a brief description of the classes:
- Main: the central class that coordinates the various modules and manages the connection with Firebase. It initializes controller, authentication, and database, handling the loading and synchronization of user presets.
- MidiController: translates messages coming from the MIDI controller and the pedal into commands the system can understand and manages events such as Note On/Off, Pitch Bend, Control Change, … .
- TouchController: manages touch interaction and mouse clicks on the interface: keys, pads, and visual controls are translated into commands that the controller processes in real time.
- Controller: acts as a bridge between input, logic, and interface.
- View: handles everything related to the system GUI, managing dynamic control updates, knob animations, … .
- Model: manages presets, instrument configurations, MIDI events, arpeggiator and drum pad. This is where audio parameters are updated and user choices are saved.
- AudioModel: represents the app’s audio engine. It manages oscillators, filters, delay, percussion sounds, and amplitude analysis for visualization. All sounds are synthetically generated through the Web Audio API.
For more in-depth info, go to GitHub.
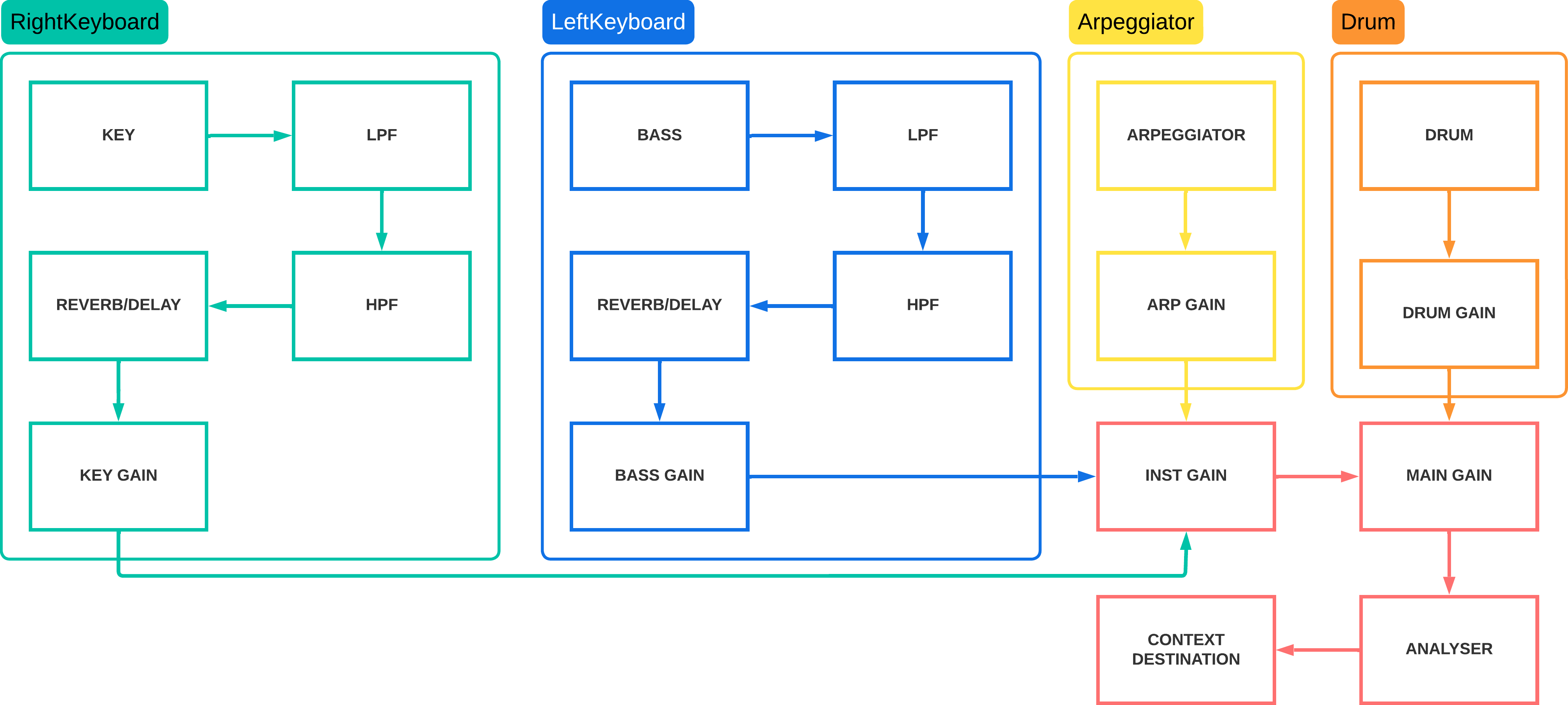
Audio chain
The entire audio chain is managed by the AudioModel class and follows the scheme below, which illustrates the sequence of filters, delay, oscillators, and gain nodes:
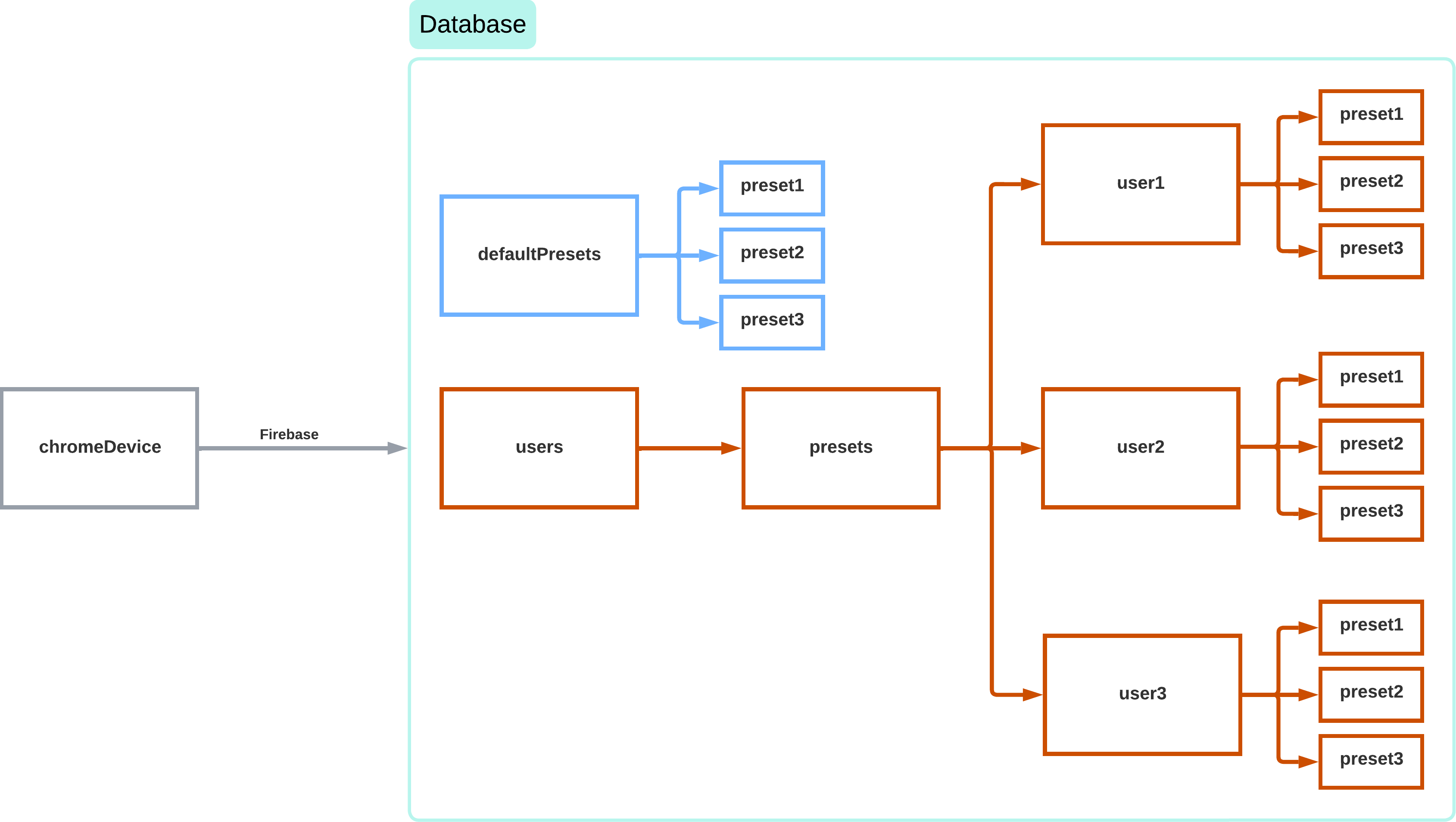
Database and authentication
The system relies on Firebase for preset management. It is possible to access the system anonymously, but in that case only the default presets will be available and it will not be possible to save new ones. To use this second option, you must log in via email and password. Access rules are managed directly on Firebase to prevent unauthorized use.
Possible improvements
I had planned the possibility to select the MIDI controller directly from a dropdown menu, in order to allow guided configuration and automatic saving of the mapping on Firebase, but I did not have enough time before the exam, and the time after the exam is also scarce. For this reason, the project is currently on hold.
In the future, when university is over, the planets align, and I have time and motivation to do it, I will finish the work.
For now, have fun (as long as you have a MiniLab MKII)!